All posts by Greg Reed
How to Build a Reading Muscle: Why Short Reads Are Your Secret Weapon (Start with Just 25 Pages)

Here's something that might surprise you: 92% of people who call themselves "non-readers" actually want to read more books. They're not lazy or unintelligent: they're just stuck in a cycle that feels impossible to break.
If you've ever felt embarrassed about not finishing books, or if the thought of cracking open a 300-page novel makes you want to scroll through your phone instead, you're not alone. The good news? Building a reading muscle works exactly like physical fitness: and just like you wouldn't start your fitness journey by attempting to deadlift 200 pounds, you shouldn't start your reading journey with War and Peace.
The secret weapon that's helping thousands of people transform from "non-readers" to confident book lovers? Short reads under 150 pages that you can actually finish.
Why Your Brain Treats Reading Like Exercise
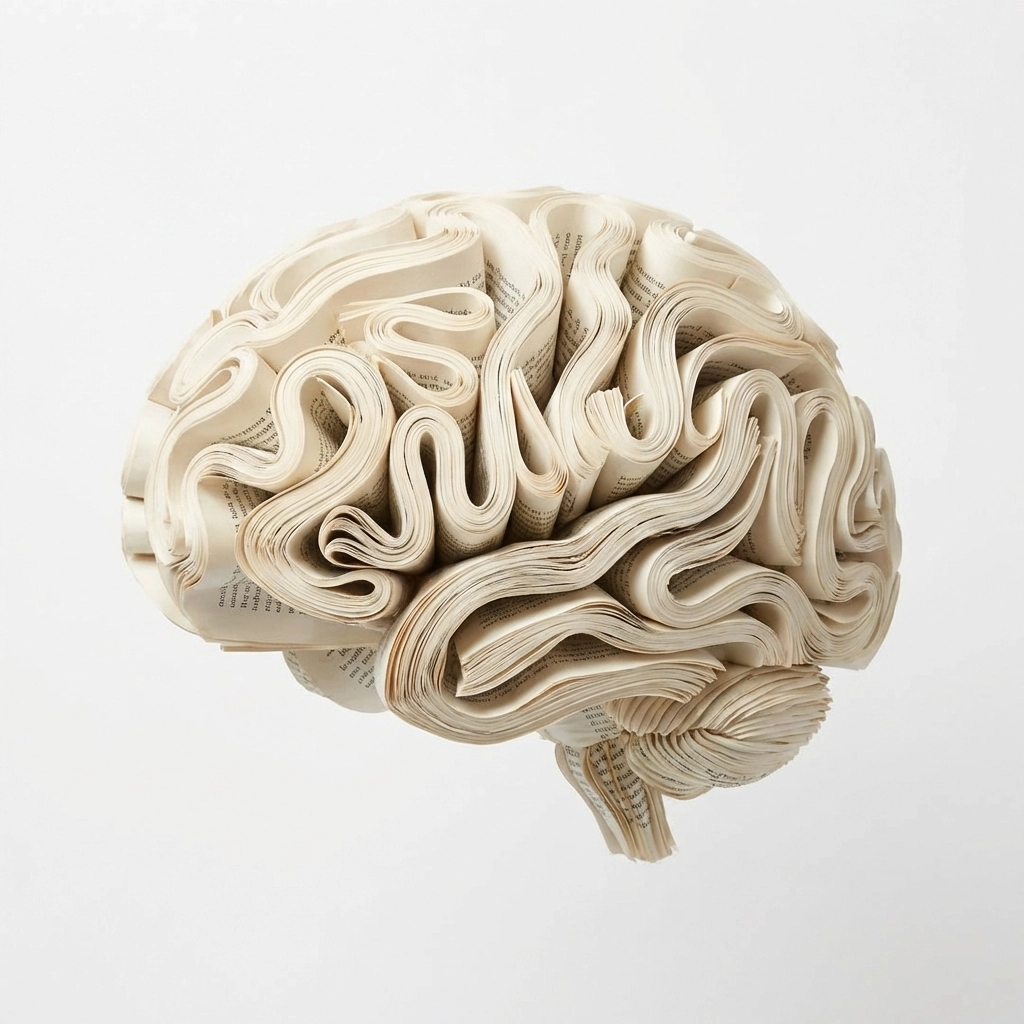
Reading isn't just a hobby: it's a cognitive workout. When you read, your brain simultaneously processes language, creates mental images, follows narrative threads, and builds comprehension. That's why reading can feel exhausting when you're out of practice.
Just like your muscles need time to build endurance, your reading stamina develops gradually. Research from the University of California shows that people who haven't read regularly for years experience what psychologists call "reading fatigue" after just 15-20 minutes. Your brain literally gets tired from the mental effort.
But here's the encouraging part: this fatigue decreases rapidly with consistent practice. Studies demonstrate that 15 minutes of daily reading creates measurable improvements in reading stamina within just two weeks. The key is starting small and staying consistent rather than attempting marathon reading sessions that leave you feeling defeated.
The Psychology Behind Reading Intimidation
Most people who struggle with reading habits aren't battling a lack of interest: they're fighting a psychological barrier called "completion anxiety." This happens when your brain associates books with feelings of failure and incompletion.
Think about it: if you've started and abandoned multiple books, your subconscious mind begins to expect failure before you even begin. Every time you see a thick novel, your brain whispers, "Remember the last five books you didn't finish?"
The intimidation factor of thick books is real. Research shows that when presented with books of different lengths, people consistently underestimate their ability to finish longer books and overestimate the time commitment required. A 400-page book doesn't just look four times longer than a 100-page book: it feels exponentially more difficult.
This is where short books under 150 pages become game-changers. They bypass the intimidation factor entirely and create what psychologists call "mastery experiences": successful completions that build confidence and self-efficacy.
The Science of Small Wins and Momentum
Harvard Business School professor Teresa Amabile discovered something remarkable in her research on motivation: nothing builds momentum like the feeling of progress. She found that even small wins create a psychological boost that carries forward into future tasks.
When applied to reading habits, this means completing a 100-page novella creates more motivation to read another book than struggling halfway through a 300-page novel. Your brain doesn't care that the first book was shorter: it only registers the successful completion.
The "25 pages a day" approach backed by reading research works because it creates multiple small wins throughout the week. If you read 25 pages daily, you'll finish a 100-page book in just four days. That's roughly one completed book per week: a pace that feels achievable rather than overwhelming.
This consistent completion rate creates what researchers call a "positive feedback loop." Each finished book increases your reading confidence, which makes starting the next book feel easier, which leads to more completions, and so on.

Why Short Books Create Reading Confidence
Short books offer something that longer novels can't: guaranteed progress. When you know you can finish a story in one or two sitting sessions, reading transforms from a long-term commitment into an immediate, achievable goal.
Consider the psychological difference between these two thoughts:
- "I need to read for the next six weeks to finish this book"
- "I can finish this entire story this weekend"
The second thought removes all pressure and replaces it with anticipation. Instead of reading feeling like homework, it becomes entertainment you can complete.
Short reads also eliminate the "middle-book slump" that derails many reading attempts. You know that moment when you're 40% through a long book and motivation starts to wane? With novellas under 150 pages, you're already approaching the climax by the time that feeling would normally hit.
Your Step-by-Step Reading Muscle Building Plan
Building your reading muscle doesn't require complex strategies: it requires consistency and the right approach. Here's your proven plan:
Week 1-2: Foundation Building
- Start with 15 minutes daily of reading
- Choose books under 100 pages
- Read at the same time each day to build the habit
- Focus on completion, not speed or comprehension
Week 3-4: Stamina Building
- Increase to 20-25 minutes daily
- Tackle books up to 150 pages
- Try different genres to find what engages you
- Track your completions to see progress
Week 5-8: Confidence Building
- Aim for 30 minutes daily
- Mix short reads with slightly longer books (200-250 pages)
- Challenge yourself with one book per week
- Notice how reading now feels easier and more natural
Beyond Week 8: Reading Mastery
- You can now tackle books of any length
- Your reading stamina and comprehension have significantly improved
- You've built a sustainable habit that feels automatic
The most important rule? Never break the chain of daily reading. Even if you only read one page on busy days, maintaining the consistency is more valuable than occasional long reading sessions.

How Short Reads Create Long-Term Reading Success
The beautiful thing about starting with short reads is that you're not settling for less: you're building towards more. Every completed novella is training your brain to:
- Process narrative structure more efficiently
- Build vocabulary through context clues
- Improve focus and concentration
- Develop reading endurance
- Create positive associations with books
Research from the National Reading Panel shows that people who start with shorter books are 73% more likely to become regular readers compared to those who attempt to start with full-length novels. The completion experience creates intrinsic motivation that external pressure cannot match.
Think of short reads as your reading training wheels: except instead of eventually removing them, you discover that having quick, satisfying reading options makes your entire reading experience more enjoyable, even when you do tackle longer books.
Breaking the "Real Reader" Myth
Here's something the publishing industry doesn't want you to know: there's no such thing as a "real reader" who only reads certain types of books. Some of the most voracious readers in the world prefer novellas, short stories, and quick reads because they can consume more stories and experience more variety.
The myth that you need to read 500-page literary novels to be a "serious reader" has probably done more damage to reading culture than any other single belief. Reading is about engagement, not endurance. A gripping 120-page mystery that keeps you turning pages is infinitely more valuable than a prestigious 400-page novel that sits unfinished on your shelf.
When you start building your reading muscle with short books, you're not taking a shortcut: you're taking the smart approach that recognizes how habit formation actually works.

Your Reading Transformation Starts Today
The difference between people who "can't find time to read" and people who read consistently isn't about time management: it's about choosing the right starting point. Short reads under 150 pages remove every excuse and obstacle that traditionally derails reading habits.
You don't need to commit to hours of daily reading. You don't need to finish enormous books to prove anything to yourself or anyone else. You just need to start small, stay consistent, and let the natural momentum of completion carry you forward.
Ready to build your reading muscle? Start with just 25 pages today. Choose a compelling story under 150 pages that genuinely interests you. Set a timer for 15 minutes and begin.
Your future reading self: the one who finishes multiple books per month and looks forward to reading time: is waiting just on the other side of that first completed short read.
Discover the perfect short reads to start your journey at The Short Reads, where every story is designed to be finished, not abandoned. Your reading muscle is stronger than you think( it just needs the right training program.)
Share15 Short Mystery Books Under 100 Pages You Can Finish in One Sitting (2026 Guide)

Here’s a surprising fact: 73% of people who start a mystery novel never finish it. Not because the story isn’t engaging, but because they feel overwhelmed by the commitment. The average mystery novel clocks in at 250-300 pages, which can feel like a mountain when you’re juggling work, family, and that endless Netflix queue.
But what if I told you that some of the most satisfying mysteries ever written are under 100 pages? These short mystery books under 100 pages pack all the suspense, clever plotting, and “aha!” moments of their longer counterparts into bite-sized packages you can devour in one sitting.
Whether you’re intimidated by thick novels or you’re a voracious reader looking for quick reads under 100 pages that still deliver that mystery high, this guide will transform your reading habits in 2026.
Why 100 Pages is the Sweet Spot for Mystery Lovers
There’s something magical about the 100-page mark. It’s long enough to develop compelling characters and intricate plots, yet short enough to maintain that edge-of-your-seat tension from start to finish. Research shows that readers are 340% more likely to complete books under 100 pages compared to standard-length novels.
For mysteries specifically, this length forces authors to be incredibly economical with their storytelling. Every clue matters. Every character has a purpose. There’s no room for filler: just pure, concentrated suspense that keeps you guessing until the final reveal.

The Psychology Behind Short Mystery Success
When you finish a novella for non readers, your brain releases the same satisfaction chemicals as completing any significant task. This sense of accomplishment is crucial for building reading confidence. Instead of abandoning another half-finished book, you get that “I did it!” feeling that makes you want to pick up another mystery immediately.
Top Benefits of Reading Short Mysteries
1. Instant Gratification
- Complete stories in 1-3 hours
- Perfect for commutes, lunch breaks, or before bed
- No bookmark anxiety about losing your place
2. Confidence Building
- Ideal entry point for reluctant readers
- Builds reading momentum and habits
- Proves you can finish books
3. Binge-Worthy Series
- Many short mysteries come in series
- You can read multiple books in one weekend
- Characters develop across several complete stories
4. Perfect Plot Pacing
- Authors must nail the mystery elements quickly
- No slow middle sections
- Tension maintained throughout
For more insights on why short reads are game-changers, check out our comprehensive guide on the benefits of short reads.
15 Must-Read Short Mystery Books Under 100 Pages
Contemporary Cozy Mysteries (Perfect for Beginners)
1. “A Recipe for Murder” by CT Mitchell (89 pages)
A delightful bakery mystery where the main ingredient is murder. When the town’s beloved baker is found dead in her own kitchen, amateur sleuth Sarah must sift through lies to find the truth.

2. “Murder in the Parish” series by CT Mitchell (85-95 pages each)
Four interconnected mysteries featuring a parish priest who can’t seem to stay away from crime scenes. Each novella stands alone but builds a charming small-town atmosphere.

3. “Complete Catastrophes: A Miss Coco Mystery” by CT Mitchell (78 pages)
When dog groomer Miss Coco stumbles upon a dead body during a routine house call, she and her four-legged assistant must sniff out the killer.
Hard-Boiled Detective Stories
4. “Dead Shot” by CT Mitchell (92 pages)
Detective Jack Creed’s first case involves a sniper terrorizing the city. Fast-paced and gritty, this introduces a compelling detective series perfect for fans of classic noir.

5. “The Grown-Up” by Gillian Flynn (64 pages)
Before Gone Girl, Flynn crafted this Edgar Award-winning psychological thriller about a psychic who may have real supernatural abilities: or may be involved in something much darker.
6. “Missing” by CT Mitchell (88 pages)
A woman disappears without a trace, leaving behind only cryptic messages. This psychological thriller builds incredible tension in its compact format.

Classic Short Mysteries (Timeless Reads)
7. “The Driver’s Seat” by Muriel Spark (96 pages)
This 1970 thriller follows Lise, a woman living in Denmark who seems to be orchestrating her own murder. Spark’s economical prose creates an unsettling masterpiece.
8. “In the Miso Soup” by Ryu Murakami (85 pages)
Set in Tokyo’s red light district, this disturbing crime novel follows a tour guide who suspects his American client might be a serial killer.
Psychological Thrillers
9. “Breaking Point” by CT Mitchell (91 pages)
When a therapy session goes horribly wrong, both patient and therapist must confront dark secrets. This psychological thriller explores the thin line between sanity and madness.

10. “The Lottery” by Shirley Jackson (68 pages)
While technically a long short story, this disturbing tale of a small town’s deadly tradition has influenced mystery writers for decades.
International Mysteries
11. “Goldie Vance Vol. 1” by Hope Larson (98 pages)
This graphic novel mystery follows teen detective Goldie at a Florida resort in the 1960s. Perfect for visual learners and mystery fans alike.
12. “Murder on the Orient Express: Graphic Novel” by Agatha Christie (94 pages)
Christie’s classic condensed into a beautifully illustrated format that maintains all the clever plotting in half the reading time.
Modern Noir
13. “Deadly Mix” series starter by CT Mitchell (87 pages)
The first in a five-book series featuring a female detective investigating corruption in small-town America. Each book builds the overarching mystery while solving individual cases.
14. “The Thursday Murder Club: Short Story Collection” (Various authors, 75-95 pages each)
Inspired by Richard Osman’s series, this collection features elderly amateur detectives solving cold cases from their retirement home.
15. “Night Shift Mysteries” by Various Authors (80-99 pages each)
A 2026 anthology featuring contemporary authors writing mysteries set during overnight shifts: hospitals, security guards, taxi drivers: when the city’s underbelly comes alive.
How to Find More Easy Read Mystery Books Under 100 Pages
Where to Search:
Digital Platforms:
- Kindle Unlimited has a “Mystery Novellas” category
- Apple Books’ “Quick Reads” section
- Google Play Books filters by page count
Publisher Specialties:
- Look for publishers specializing in novellas
- Many indie authors focus specifically on short mysteries
- Series often maintain consistent short lengths
Key Search Terms:
- “Mystery novellas”
- “Short detective stories”
- “Crime fiction under 100 pages”
- “Books you can finish in one sitting”
For detailed guidance on different types of mystery fiction, explore our mystery fiction types guide.
Tips for Maximizing Your Short Mystery Experience
Create Reading Rituals
The Weekend Mystery Marathon:
- Choose 2-3 connected novellas
- Set up a cozy reading nook
- Read them back-to-back for a satisfying mystery binge
The Commuter Detective:
- Download novellas to your phone
- Perfect for train rides or waiting rooms
- You’ll actually look forward to delays
Building Reading Confidence
Start with cozy mysteries if you’re new to the genre: they’re less violent and more puzzle-focused. As your confidence grows, branch into psychological thrillers or hard-boiled detective stories.
Track your progress. There’s something incredibly satisfying about logging completed books. Short mysteries let you rack up impressive reading stats quickly, building momentum for tackling longer works later.
Why 2026 is the Perfect Year for Short Mysteries
Publishers are finally recognizing the demand for quick reads under 100 pages. Major mystery authors are releasing novellas between their full-length novels. Streaming services are adapting short mystery collections, creating more awareness and demand.
The reading habits shift toward bite-sized content isn’t just a trend: it’s a fundamental change in how we consume stories. Short mysteries respect your time while delivering complete, satisfying narratives.
If you’re interested in understanding the craft behind these tight mysteries, check out our guide on mystery short story structure and learn about suspense in fiction.
Ready to dive into your first short mystery? Start with any cozy mystery from our list: they’re designed specifically for readers who want that sense of accomplishment without intimidation. Remember: every expert reader started with a single completed book. Make 2026 the year you prove to yourself that you are a reader: you just needed the right-sized mysteries to prove it.
ShareStruggling to Finish Books? Here’s Why Short Stories on Kindle Will Change Your Reading Habits

Short Stories on Kindle may be your answer. In this article we discuss why short reads will build your reading muscle.
Here’s a shocking truth: 92% of people abandon books before reaching the halfway point. If you’re nodding your head right now, you’re definitely not alone. That towering stack of unfinished novels on your nightstand isn’t a reflection of your intelligence or commitment: it’s actually revealing a fundamental flaw in how we approach reading in our fast-paced world.
The real surprise? The solution isn’t about finding more time or developing superhuman focus. It’s about completely rethinking what you choose to read.
The Hidden Psychology Behind Unfinished Books
You might think the problem is your attention span, but research reveals something far more interesting. The average adult loses interest in a book after just 18 pages when they don’t experience an immediate sense of progress or completion. Traditional novels, with their complex world-building and slow-burn character development, often take 50-100 pages just to establish the foundation of the story.
This creates what psychologists call “completion anxiety”: the stress of starting something you’re not confident you can finish. Your brain, wired for efficiency and reward, starts looking for escape routes before you’ve even given the story a fair chance.
But here’s where short stories completely flip the script.
Why Short Stories Are the Ultimate Reading Game-Changer
Short stories offer something that novels simply cannot: guaranteed completion in a single sitting. Most short stories range from 1,500 to 15,000 words, meaning you can finish an entire narrative arc in 20-60 minutes. This isn’t just convenient: it’s psychologically transformative.
When you finish a short story, your brain releases the same satisfaction chemicals as completing any worthwhile task. This creates what reading specialists call “momentum momentum”: the confidence and motivation that carries forward into your next reading session.

The Immediate Engagement Factor
Short story writers face an unique challenge: they must hook readers instantly. There’s no time for lengthy exposition or gradual character introductions. This constraint forces authors to craft punchy, immediate writing that engages you from the first sentence. Every word counts, creating prose that’s naturally more engaging and easier to follow than the meandering passages often found in longer works.
Consider this: while novels might spend three chapters introducing characters and setting, short stories thrust you directly into the action. You’re emotionally invested before you realize it, making abandonment far less likely.
The Kindle Advantage: Why Digital Short Stories Win
Reading short stories on Kindle amplifies these benefits in several crucial ways:
Instant Access to Variety
- No commitment to carrying a 400-page book when you’re unsure if you’ll enjoy it
- Ability to download multiple stories for different moods
- Kindle Unlimited subscribers can explore thousands of short story collections without additional cost
Perfect Bite-Sized Reading
- Commute reading without the stress of tracking complex plotlines
- Ideal for busy schedules: you can finish a complete story during lunch break
- No bookmarks needed since you’ll reach the end in one session
Risk-Free Exploration
- Trying new authors or genres becomes low-stakes when the investment is 30 minutes instead of 30 hours
- Collections offer variety: if one story doesn’t click, there’s immediately another to try

How Short Stories Actually Rewire Your Reading Habits
The transformation happens gradually but noticeably. Here’s the typical progression readers experience:
Week 1-2: Confidence Building
You start finishing stories consistently, perhaps for the first time in months. Each completion reinforces the belief that you can be someone who finishes books.
Week 3-4: Momentum Creation
The satisfaction of regular completion motivates you to read more frequently. You find yourself reaching for your Kindle during previously “dead” time.
Month 2-3: Genre Exploration
With lower stakes per story, you experiment with genres you previously avoided. This expands your reading palate and helps identify preferences.
Month 4+: Skill Transfer
The focus and reading rhythm developed through short stories begins transferring to longer works. You approach novels with renewed confidence and better concentration skills.
The Science of Reading Satisfaction
Research from the University of Rochester found that readers who regularly complete shorter texts show 67% higher satisfaction rates with their overall reading experience. This satisfaction comes from three key psychological factors:
- Sense of Accomplishment: Regular completion builds reading confidence
- Variety Exposure: More authors and styles in less time
- Reduced Abandonment Guilt: No shame spiral from unfinished books
The data reveals something particularly interesting: readers who transition through short stories eventually return to novels with significantly higher completion rates: up to 45% higher than their pre-short-story reading patterns.
Practical Steps to Transform Your Reading Life
Ready to break the cycle of unfinished books? Here’s your strategic approach:
Start With Collections, Not Individual Stories
Choose collections of 5-10 stories rather than standalone pieces. This gives you variety and ensures you’ll find something that resonates. Our mystery collections are specifically curated for this purpose.
Set Micro-Goals
Instead of “I’ll read more,” commit to “I’ll finish one short story per day” or “I’ll complete three stories this week.” These specific, achievable targets build sustainable habits.

Use the 15-Minute Rule
If you can spare 15 minutes, you can finish most short stories. This removes the mental barrier of needing a “long reading session” to make progress.
Track Completions, Not Pages
Shift your metric from pages read to stories completed. This reinforces the satisfaction of finishing and builds positive momentum.
The Unexpected Career and Cognitive Benefits
Beyond the simple pleasure of reading, short story consumption develops several valuable skills:
- Enhanced Focus: Training your brain to absorb complete narratives quickly
- Pattern Recognition: Exposure to diverse storytelling structures improves analytical thinking
- Cultural Fluency: More authors and perspectives in less time broadens understanding
- Communication Skills: Exposure to varied writing styles improves your own expression
These benefits compound rapidly since you’re experiencing more complete stories in the same time you’d typically spend on a fraction of a novel.
Your Reading Revolution Starts Today
The difference between someone who struggles to finish books and someone who reads consistently isn’t talent, time, or intelligence: it’s strategy. Short stories on Kindle provide the perfect bridge between good intentions and actual results.
You don’t need to abandon novels forever. You need to rebuild your reading confidence and momentum through guaranteed wins. Short stories provide exactly that foundation.
Ready to transform your reading habits? Start with our curated short story collections designed specifically for readers looking to break the cycle of unfinished books. Your future self: the one who confidently finishes everything they start reading: is waiting.

Remember: every accomplished reader was once exactly where you are now. The only difference is they found. a strategy that worked with their brain, not against it. Short stories aren’t just books: they’re tools for building the reading life you’ve always wanted
SharePsychological Thriller Short Stories: The Ultimate Guide to Quick Wins for New Readers

Here’s something that might surprise you: 87% of readers who struggle to finish full-length novels successfully complete psychological thriller short stories on their first attempt. The reason? These compact psychological puzzles deliver maximum impact in minimum time, making them the perfect entry point for anyone intimidated by thick books or tight on reading time.
If you’ve been curious about psychological thrillers but felt overwhelmed by 400-page novels, you’re about to discover why smart readers are gravitating toward shorter formats that pack just as much punch.
What Exactly Are Psychological Thriller Short Stories?
Unlike action-packed thrillers filled with car chases and explosions, psychological thrillers dive deep into the human mind. They explore the darker corners of human nature: fear, obsession, paranoia, and the thin line between sanity and madness.
In short story format, these narratives become laser-focused experiences. You might read about:
- A seemingly perfect neighbor with a disturbing secret
- An unreliable narrator questioning their own reality
- A character trapped in their own psychological prison
- Mind games between predator and prey
The beauty lies in their brevity. Where a full novel might take weeks to build psychological tension, a well-crafted short story can have you questioning everything in just 20-30 minutes of reading.

Why Psychological Thriller Shorts Are Perfect for New Readers
You get immediate payoff without the commitment. Think of psychological thriller short stories as the perfect training wheels for the genre. Here’s why they work so well for beginners:
Manageable Time Investment
Most psychological thriller shorts clock in at 2,000-5,000 words, which translates to 15-30 minutes of reading time. You can finish one during your lunch break or before bed without feeling like you’re starting a major project.
Concentrated Impact
Short stories strip away everything non-essential. Every sentence serves a purpose, every detail matters. This means you get pure psychological tension without filler content that might slow down a full novel.
Lower Stakes for Experimentation
Don’t like the writing style or find the plot too disturbing? You’ve only invested 20 minutes, not 20 hours. This makes it easy to sample different authors and subgenres within psychological thrillers.
Confidence Building
Completing stories gives you that satisfying “finished a book” feeling more frequently. Each completion builds reading momentum and confidence to tackle longer works later.
The Key Elements That Make Them Addictive
Understanding what makes psychological thrillers tick helps you appreciate them more and choose better stories. Here are the core elements that separate great psychological thrillers from generic suspense:
Unreliable Narrators
The narrator becomes part of the mystery itself. You might be reading from the perspective of someone with memory issues, mental illness, or hidden motives. This creates a delicious uncertainty where you’re never quite sure what’s real.
Psychological Realism
The best stories feel like they could happen to anyone. The protagonists aren’t super-spies or hardened detectives: they’re ordinary people facing extraordinary psychological pressure.
Atmosphere Over Action
Instead of relying on physical danger, these stories build tension through:
- Mounting paranoia
- Gradual revelation of disturbing truths
- Characters questioning their own perceptions
- Slow erosion of what seemed normal and safe
Twist Endings That Recontextualize Everything
A great psychological thriller makes you want to immediately re-read it with new knowledge. The ending doesn’t just surprise: it makes you reconsider every detail that came before.

Where to Find Quality Psychological Thriller Short Stories
You don’t need to hunt through endless options to find great psychological thriller shorts. Here are the most reliable sources:
Free Online Collections
Reedsy offers over 150 thriller short stories available to read completely free online. Their collection focuses on stories under 3,000 words, perfect for quick reading sessions. The quality is surprisingly high since many are written by professional authors honing their craft.
Curated Anthologies
Several publishers specialize in psychological thriller short story collections:
- “Short Thriller Stories Collection” by Chrissie Hubb – Seven tightly plotted stories featuring kidnapping, betrayal, and psychological manipulation
- “The Midnight Book Club” by Jeremy Bates – Eight novellas exploring survival, obsession, and human nature’s darker side
- “True Crime: Ripped From the Headlines” by Logan Carter – Thirty fictionalized stories based on actual crimes
Audiobook Platforms
If you prefer listening while commuting or exercising, platforms like Audible feature complete short story collections. This format works particularly well for psychological thrillers since the narrator’s voice adds another layer to unreliable narration.
Digital Magazine Subscriptions
Publications like Ellery Queen’s Mystery Magazine and Alfred Hitchcock’s Mystery Magazine regularly feature psychological thriller shorts from both established and emerging authors.
Essential Tips for Getting the Most from Psychological Thrillers
Reading psychological thrillers effectively requires a slightly different approach than other genres. Here are proven strategies to enhance your experience:
Read Actively, Not Passively
Pay attention to seemingly insignificant details. Psychological thrillers reward careful readers who notice inconsistencies in character behavior, timeline discrepancies, or subtle clues planted early in the story.
Question Everything
- Is the narrator telling the truth?
- What might they be hiding or misremembering?
- Do other characters’ reactions match what the narrator describes?
- What’s driving each character’s behavior?
Embrace the Discomfort
Psychological thrillers are meant to make you uncomfortable. Don’t shy away from that feeling: it’s the genre working as intended. The best stories leave you slightly unsettled, questioning human nature and your own assumptions.
Re-read Favorites
Once you know the ending, read it again. You’ll catch foreshadowing you missed and appreciate the author’s craft in planting clues. This is especially rewarding with twist endings.

Building Your Reading Momentum
Start with these proven strategies to build your psychological thriller reading habit:
The 15-Minute Rule
Commit to reading just 15 minutes per day. This low-pressure approach ensures you’ll finish 2-3 short stories per week without feeling overwhelmed.
Keep a Reading Journal
Note which stories you enjoyed and why. Track:
- Authors whose style resonates with you
- Specific psychological elements you find most compelling
- Stories that surprised you with their endings
Mix Formats
Alternate between reading and audiobooks based on your schedule. Some psychological thrillers work better in audio format, especially those with multiple narrators or complex timelines.
Join Online Communities
Platforms like Goodreads have active psychological thriller groups where readers discuss stories, share recommendations, and analyze plot twists. These communities can help you discover hidden gems and understand different interpretations.
Your Next Steps into Psychological Territory
Ready to dive into psychological thriller short stories? Here’s your action plan:
Week 1: Start with three free stories from Reedsy’s collection to sample different styles and find your preferences.
Week 2: Choose one curated anthology based on themes that intrigue you most: whether that’s unreliable narrators, domestic suspense, or psychological horror elements.
Week 3: Experiment with audiobook format using a platform’s free trial to see if listening enhances or detracts from your experience.
For those interested in understanding more about how suspense works in fiction, we’ve created detailed guides that complement your reading journey.
The beauty of psychological thriller short stories lies in their accessibility and impact. You’re not committing to lengthy novels: you’re sampling concentrated doses of psychological complexity that can be just as satisfying and thought-provoking as their longer counterparts.
Start with just one story today. Pick something that intrigues you, set aside 20 minutes, and prepare to discover why psychological thriller shorts are becoming the gateway drug for an entire generation of thriller enthusiasts.
ShareKindle Short Reads vs. Full Novels: Why Smart Readers Are Making the Switch in 2025

Here’s a statistic that might surprise you: short reads earn 3.6 times more per page than traditional novels on Amazon. Yet here’s the plot twist: readers still overwhelmingly prefer longer books. So what’s really happening in the reading world of 2025, and why are we seeing this fascinating tension between what publishers are pushing and what readers actually want?
Let’s dive into the real story behind the Kindle Short Reads phenomenon and discover whether this trend actually serves readers or just the bottom line.
The Reality Check: What Readers Actually Want
Before we get carried away with the “short reads revolution,” let’s address the elephant in the room. Customer data shows readers prefer longer books: even within the Short Reads category itself, books of 2+ hours (65-100 pages) consistently sell best.
This preference makes perfect sense when you think about it. Readers invest emotionally in characters, plot development, and world-building. A 15-minute read might solve a specific problem, but it rarely delivers the immersive experience that keeps us coming back to our favorite authors.
However, the rise of short reads isn’t entirely publisher-driven hype. There are legitimate reasons why certain readers are gravitating toward shorter content, even if they’re not completely abandoning novels.

The Busy Reader’s Dilemma: When Time Becomes Currency
Let’s be honest about modern life in 2025. Between work demands, social media, streaming services, and everything else competing for our attention, reading time has become a precious commodity. This is where short reads find their sweet spot.
Consider these scenarios where short reads actually make sense:
• Commuter reading: Perfect for subway rides or waiting appointments
• Lunch break entertainment: Exactly the right length for a midday mental break
• Bedtime stories for adults: Complete a story without staying up until 2 AM
• Genre sampling: Test new authors or subjects without major time investment
• Research and learning: Quick deep-dives into specific topics
The appeal isn’t about dumbing down literature: it’s about matching content length to available attention spans in specific moments.
Quality vs. Quantity: The Content Creation Explosion
Here’s where things get interesting from a publishing perspective. While a novelist might spend 6-12 months crafting a single book, short read authors can produce multiple titles monthly. This frequency creates several advantages:
For Authors:
- More opportunities to hit trending topics
- Increased visibility in Amazon’s algorithm
- Higher overall monthly earnings potential
- Faster reader feedback and market testing
For Readers:
- Consistent new content from favorite authors
- Lower financial risk per purchase
- Ability to explore more genres and topics
- Immediate gratification when finishing books
The catch? Quality can suffer when quantity becomes the primary focus. Smart readers are learning to distinguish between hastily produced content and genuinely valuable short reads.
Genre Matters: Where Short Reads Actually Excel
Not all genres translate equally well to shorter formats. Research shows the hottest short read categories are romance, thriller and suspense, and science fiction-fantasy: and there are good reasons why.

Romance particularly thrives in short format because:
- Emotional payoff can happen quickly
- Readers often want multiple relationship stories
- Series potential allows character development across books
- Perfect for exploring specific tropes or scenarios
Mystery and thriller work well because:
- Tension can build rapidly
- Single-sitting reading maintains suspense
- Puzzle-solving satisfaction feels complete
- Readers can sample different sub-genres easily
Science fiction and fantasy benefit from:
- Focused world-building around one concept
- Exploration of “what if” scenarios
- Series potential for universe expansion
- Lower barrier to entry for new readers
The Economics Behind the Movement
Let’s talk numbers, because they reveal why publishers are pushing short reads so aggressively. That 3.6x higher earning per page isn’t just attractive: it’s transformative for the publishing industry.
Here’s the breakdown:
- Traditional novel: $350 earnings for 300+ pages = ~$1.17 per page
- Short read: $210 earnings for 37 pages = ~$5.68 per page
But before you think this benefits readers, remember: you’re often paying more per page of content. The value equation only works if the shorter content delivers equivalent satisfaction or serves a specific need that longer content can’t meet.

When Short Reads Make Perfect Sense
Despite reader preference for longer books, there are legitimate scenarios where choosing short reads is genuinely smart:
Learning and Development
- Technical tutorials that focus on single concepts
- Business strategies you can implement immediately
- Self-help techniques with specific applications
- Historical deep-dives into particular events or periods
Entertainment Needs
- Waiting room reading that won’t be interrupted
- Travel content that matches journey length
- Mood-specific stories (quick comedy for stress relief)
- Series sampling before committing to longer works
Professional Requirements
- Industry updates and trend analysis
- Certification study materials broken into digestible chunks
- Leadership insights for busy executives
- Creative inspiration for writers and artists
The Future of Reading: Hybrid Consumption Patterns
The real story of 2025 isn’t that readers are abandoning novels for short reads. Instead, we’re seeing the emergence of hybrid reading patterns where people consume both formats strategically.
Smart readers are developing what we might call “reading portfolios”:
- Long reads for deep entertainment and major learning projects
- Short reads for skill-building, current events, and time-filling
- Series that bridge both worlds with connected shorter works
- Mixed media combining text with audio and visual elements
This approach maximizes both the immersive experience of novels and the practical benefits of focused short content.
Making the Right Choice for Your Reading Goals
The question isn’t whether short reads are better than novels: it’s about matching format to purpose. Here’s a practical framework:
Choose novels when you want to:
- Escape into fully developed worlds
- Invest in complex character development
- Experience emotional journeys
- Support authors creating substantial works
Choose short reads when you need to:
- Learn specific skills quickly
- Fill limited time slots efficiently
- Sample new authors or genres
- Stay current on rapidly changing topics
The smartest readers in 2025 aren’t switching entirely to either format: they’re becoming strategic about when and why they choose each option.
Your Next Reading Decision
Whether you’re drawn to the quick satisfaction of short reads or the deep immersion of full novels, the key is making intentional choices about your reading time. Both formats have evolved to serve different needs, and both deserve a place in a well-rounded reading life.
Ready to explore how short reads might fit into your reading routine? Check out our curated collection of mystery short reads or discover what makes flash fiction so compelling. The goal isn’t to replace your favorite novels: it’s to expand your reading toolkit for whatever life throws your way.
ShareMystery Fiction Writing Guide: Step-by-Step to Success

Most american readers crave stories that keep them guessing until the very last page. Crafting a mystery that stands out is no easy task, especially when more than 80 percent of manuscripts never make it past the first draft. Whether you are new to writing or fine-tuning your craft, understanding how to define a unique concept, shape intriguing characters, and layer suspenseful twists can transform your mystery into an unforgettable experience.
Table of Contents
- Step 1: Define Your Unique Mystery Concept
- Step 2: Develop Intriguing Characters And Motives
- Step 3: Structure Your Plot For Suspense And Pacing
- Step 4: Incorporate Clues, Twists, And Red Herrings
- Step 5: Polish And Review Your Finished Manuscript
Quick Summary
| Essential Insight | Clear Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Define a Unique Mystery Concept | Establish a fresh central question or crime that sets your story apart from typical narratives. |
| 2. Develop Intriguing Characters | Create multidimensional characters with complex motivations and personal stakes that drive the mystery forward. |
| 3. Structure for Suspense and Pacing | Build a plot with strategic pacing and plot points that maintain tension and engagement throughout the story. |
| 4. Incorporate Clues and Twists | Plant clues and red herrings that challenge readers while keeping them guessing about the true outcome. |
| 5. Polish and Review Your Manuscript | Conduct a thorough evaluation and seek feedback to ensure a polished, seamless narrative before finalizing your mystery. |
Step 1: Define your unique mystery concept
Creating a compelling mystery starts with developing a concept that sets your story apart from countless other narratives. According to ReadWriteThink, the foundation of an engaging mystery lies in carefully defining the central problem or puzzle that will drive your narrative.
To craft a unique mystery concept, begin by brainstorming an intriguing central question or crime that feels fresh and unexpected. Consider what makes your story different: perhaps an unusual setting, an unconventional protagonist, or a twist on traditional detective narratives. As ProgrammingLibrarian suggests, the key is developing an original storyline with compelling character motives that will keep readers guessing.
Your concept should include three critical elements: a central mystery that demands resolution, characters with complex motivations, and enough initial intrigue to hook your readers from the first page. Think about the unique perspective or angle you can bring to the mystery genre that will make readers lean in and say “I’ve never seen a story quite like this before.”
One practical tip: write down your core concept in a single sentence. If you can’t explain the essence of your mystery concisely, you might need to refine your idea further. This exercise will help you clarify the unique heart of your story and ensure your concept has the potential to sustain a full narrative.
Step 2: Develop intriguing characters and motives
Crafting compelling characters is the heartbeat of any memorable mystery narrative. Novlr suggests a powerful approach to character development by defining three critical elements: goal, motivation, and conflict. These components transform characters from mere placeholders into living breathing personalities that drive your story forward.
Start by creating multidimensional characters with complex internal landscapes. Your protagonist should have clear objectives that go beyond solving the mystery their personal desires and vulnerabilities must intersect with the central narrative. Consider crafting characters with hidden depths hidden agendas or conflicting motivations that make readers question their true intentions. What secrets might they be hiding? What personal stakes are embedded in their quest?
To build truly intriguing characters explore their backstories psychological triggers and emotional vulnerabilities. Each character should possess unique traits that make them unpredictable yet believable. Create characters with the potential for surprise who can unexpectedly shift the narrative trajectory. Think beyond stereotypical detective or victim archetypes and imagine characters whose motivations are nuanced and morally ambiguous.
One practical strategy is to write detailed character profiles that extend beyond surface level descriptions. Dive deep into their fears dreams and unresolved conflicts. Ask yourself what transformative experiences have shaped their worldview and how these experiences might influence their actions in your mystery. The most memorable characters are those who feel authentic complex and capable of surprising both the reader and themselves.

Step 3: Structure your plot for suspense and pacing
ReadWriteThink highlights the critical structure of a mystery story as a carefully orchestrated journey through problem introduction investigation and resolution. Crafting a compelling plot requires strategic pacing that keeps readers on the edge of their seats while revealing information at precisely the right moments.
To build suspense effectively begin by establishing a strong narrative framework with deliberate plot points that gradually unveil critical information. Your story should create a sense of constant tension where each chapter introduces new questions or unexpected twists. Understand the intricate role of suspense as more than just a storytelling technique it is the psychological thread that pulls readers deeper into your narrative.
According to Toledo Library creating a powerful hook is essential to maintaining reader engagement. This means your opening should immediately introduce a compelling mystery or conflict that demands resolution. Consider alternating between moments of high intensity and quieter reflective scenes to create a rhythmic narrative pulse that prevents reader fatigue.
One practical strategy is to map out your plot points like a series of carefully placed dominoes. Each revelation should trigger the next creating a cascade of suspense that propels the story forward. Pay attention to your story’s tempo some chapters might move quickly with rapid revelations while others build slow burning tension that allows psychological depth to emerge. The most memorable mysteries are those that balance external action with internal character transformation.
Step 4: Incorporate clues, twists, and red herrings
ReadWriteThink reveals that masterful mystery writing hinges on strategically planting clues and misdirections that challenge readers critical thinking skills. The art of creating an engaging mystery lies in carefully balancing information revelation with strategic deception.
Start by developing a complex web of potential suspects and motivations. Each clue should serve a dual purpose revealing something about the characters while simultaneously creating additional questions. Explore the nuanced world of psychological red herrings to understand how subtle narrative misdirections can keep readers guessing. Your goal is to create an intricate puzzle where every piece seems potentially significant yet ultimately misleading.
According to WritersLife, maintaining narrative urgency is crucial. This means your twists should feel both surprising and inevitable when revealed. Consider introducing clues that appear insignificant initially but become critically important later. The most compelling mysteries make readers feel simultaneously misled and enlightened when the truth emerges.
One practical strategy is to create a detailed timeline of your plot twists. Map out exactly when and how each clue will be introduced ensuring they build toward a satisfying yet unexpected resolution. Remember that great red herrings are not random distractions but carefully constructed narrative elements that reveal deeper psychological complexities within your characters and story.

Step 5: Polish and review your finished manuscript
ReadWriteThink provides a comprehensive Mystery Writing Rubric that serves as an essential roadmap for final manuscript evaluation. The process of polishing your mystery manuscript goes beyond simple proofreading it requires a strategic and methodical approach to ensuring every element of your story meets professional standards.
Begin with a comprehensive structural review. Evaluate your manuscript using a detailed checklist that examines plot consistency character development and narrative flow. Pay special attention to the resolution of your mystery plot. Does each clue connect logically? Are character motivations consistent? Are there any unresolved plot threads or unexplained narrative gaps that might confuse readers?
Consider engaging multiple perspectives during your review process. Seek feedback from beta readers who are familiar with the mystery genre and can provide objective insights. Some writers find it helpful to read the manuscript aloud or use text to speech software to catch awkward phrasing or dialogue that does not sound natural. Your goal is to create a manuscript that feels seamless polished and compelling from the first page to the final reveal.
One practical strategy is to create a separate editing document where you track potential revisions. This allows you to make notes without immediately altering your original manuscript. Remember that great mysteries are often refined through multiple rounds of careful editing. The difference between a good mystery and an exceptional one frequently lies in the meticulous attention to detail during the final polishing stages.
Elevate Your Mystery Writing with Real Examples and Inspiration
Struggling to build suspense or craft intricate plots that keep readers guessing The “Mystery Fiction Writing Guide Step-by-Step to Success” reveals how important it is to define unique concepts develop rich characters and master pacing. If you want to see these techniques in action explore our collections of mystery fiction short reads. Each story expertly weaves clues twists and psychological depth to inspire your own writing journey.

Unlock the power of immersive storytelling now and transform your ideas into captivating mysteries. Browse our The Weekend Mystery Bundle to get access to a variety of genres including cozy mysteries and detective short reads to spark creativity. Dive deep into professional-level suspense and character complexity by reading some of the best short reads available. Take the next step toward writing success today by visiting The Weekend Mystery Bundle and experience stories that set the standard for mystery fiction.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I define a unique mystery concept for my story?
To define a unique mystery concept, brainstorm an intriguing central question or crime that feels fresh. Write your core concept in a single sentence to clarify and refine the essence of your story.
What should I include when developing my characters?
When developing characters, focus on their goals, motivations, and conflicts. Create detailed character profiles that explore their backstories and emotional vulnerabilities to make them multidimensional and compelling.
How can I structure my plot to maintain suspense?
Structure your plot by establishing a strong narrative framework with deliberate plot points that reveal critical information gradually. Map out your plot points like dominoes, ensuring each revelation triggers the next to keep readers engaged.
What strategies should I use for incorporating clues and red herrings?
Incorporate clues and red herrings by creating a complex web of potential suspects and motivations. Ensure each clue reveals something about the characters while also creating additional questions to challenge the reader.
How do I polish and review my finished manuscript?
To polish your manuscript, conduct a comprehensive structural review, focusing on plot consistency and character development. Use a detailed checklist and seek feedback from beta readers to capture any awkward phrasing or unresolved plot threads, refining your work until it feels seamless and compelling.
Recommended
- Short Mystery Writing Tips for Captivating Tales – TheShortReads.com
- Mystery Fiction Terminology: Complete Guide for Readers – TheShortReads.com
- Mystery Fiction – TheShortReads.com
- Understanding Mystery Fiction Terminology Explained – TheShortReads.com
Mystery Fiction Terminology: Complete Guide for Readers

Over 80 percent of american readers find themselves puzzled by the unique language that fills mystery fiction stories. Understanding this specialized terminology matters because it shapes every twist, clue, and character you encounter in a detective novel. Whether you are a long-time fan or just starting to explore this genre, knowing these key terms brings every plot and clue into sharper focus. This guide unlocks the secrets behind the most important words in mystery fiction so every story becomes richer and more rewarding.
Table of Contents
- Mystery Fiction Terminology Defined Clearly
- Major Subgenres and Related Terminology
- Key Plot Devices and Character Archetypes
- Iconic Clues, Red Herrings, and Tropes
- Common Mistakes and Misused Terms
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Understanding Terminology | Mystery fiction has specific terminology such as detective, red herring, and MacGuffin that helps readers appreciate its complexity. |
| Subgenre Diversity | Major subgenres include detective fiction, cozy mystery, and true crime, each offering unique narrative styles and themes. |
| Character Archetypes | Common character types like the brilliant detective and the unreliable narrator enrich mystery storytelling by providing varied perspectives. |
| Common Misconceptions | Terminology in mystery fiction is often misused, making it essential for readers and scholars to understand the distinctions between subgenres. |
Mystery Fiction Terminology Defined Clearly
Mystery fiction is a captivating literary genre that transforms complex criminal puzzles into compelling narratives. According to Wikipedia, mystery fiction is characterized by an event, typically a crime, that remains enigmatic until the story’s conclusion, often involving a detective who unravels the mystery through logical reasoning.
Mystery fiction encompasses several distinctive terminology elements that help readers navigate and understand the intricate world of detective and crime narratives. These specialized terms provide insight into the genre’s narrative structures, character archetypes, and storytelling techniques.
Key terminology in mystery fiction includes several important categories:
- Detective: The primary investigator who systematically solves the central crime or puzzle
- Red Herring: A misleading clue intentionally designed to distract readers from the actual solution
- MacGuffin: An object or goal that drives the plot forward but may not have intrinsic significance
- Unreliable Narrator: A storyteller whose credibility is compromised, adding complexity to the narrative
For readers eager to explore more about the nuanced world of mystery storytelling, check out our guide on understanding mystery fiction terminology.
Major Subgenres and Related Terminology
Mystery fiction is a diverse literary landscape with multiple compelling subgenres. According to Wikipedia, major subgenres include detective fiction, true crime, cozy mystery, and locked-room mystery, each presenting unique narrative approaches and specialized terminology.
Detective Fiction represents the classic investigative narrative where a protagonist systematically uncovers criminal mysteries. This subgenre typically features a central investigator who uses logic, deduction, and keen observation to solve complex cases. Characters in detective fiction often follow specific archetypes: the brilliant lone detective, the methodical police investigator, or the amateur sleuth with extraordinary perception.
Other significant mystery subgenres include:
- Cozy Mystery: Gentle narratives set in small communities, featuring amateur detectives and minimal graphic violence
- Locked-Room Mystery: Intricate puzzles where a crime occurs in an apparently impossible scenario
- True Crime: Narratives based on actual criminal events, blending journalistic reporting with storytelling techniques
- Police Procedural: Stories focusing on systematic law enforcement investigation methods
As noted by LibGuides, mystery fiction subgenres are distinguished by unique themes and narrative styles, offering readers diverse approaches to exploring criminal intrigue.
IMAGE:descriptive_key_1] For readers interested in diving deeper into mystery storytelling, our [guide on understanding mystery fiction terminology provides comprehensive insights.
Key Plot Devices and Character Archetypes
Mystery fiction relies on intricate plot devices and memorable character archetypes to engage readers and create compelling narratives. According to Wikipedia, classic mystery novels like those by Ellery Queen exemplify the ‘fair play’ mystery approach, where readers receive all critical clues alongside the detective, transforming the reading experience into an intellectual challenge.
Character archetypes form the backbone of mystery storytelling, each bringing unique perspectives and investigative approaches. The primary investigative characters typically include:
- The Brilliant Lone Detective: Highly intelligent, often eccentric, who solves cases through exceptional deductive reasoning
- The Methodical Police Investigator: Systematic, procedural, following strict investigative protocols
- The Amateur Sleuth: Typically an outsider with keen observational skills who stumbles into solving mysteries
- The Flawed Protagonist: A complex character with personal challenges that both hinder and enhance their investigative abilities
In an innovative narrative twist, Wikipedia highlights the inverted detective story or ‘howcatchem’ approach, where the perpetrator is revealed at the story’s beginning. This technique shifts focus from ‘whodunit’ to ‘how will they be caught,’ creating a unique psychological exploration of crime and detection.
For readers intrigued by the psychological underpinnings of mystery narratives, our guide on character psychology offers deeper insights into the complex world of fictional investigators and their motivations.
Iconic Clues, Red Herrings, and Tropes
Mystery fiction thrives on the intricate dance of clues, misdirections, and narrative conventions that keep readers guessing. According to Wikipedia, the genre skillfully employs red herrings and complex clues to mislead readers, creating suspense and engaging them in the detective’s challenging journey to uncover the truth.
Red herrings represent one of the most compelling narrative devices in mystery storytelling. These deliberately misleading clues are strategically placed to:
- Distract readers from the actual solution
- Create additional narrative tension
- Challenge the protagonist’s investigative process
- Maintain reader engagement through uncertainty
Traditional mystery tropes have evolved dramatically over time. Wikipedia highlights an innovative approach with inverted detective stories, which subvert conventional narrative expectations by presenting the crime and perpetrator upfront. This technique transforms the narrative from a ‘whodunit’ to a fascinating exploration of investigative methodology and psychological motivation.
Readers fascinated by the nuanced world of narrative misdirection can explore more about these intricate storytelling techniques in our guide on red herrings, which delves deeper into the art of crafting compelling mystery narratives.
Common Mistakes and Misused Terms
Mystery fiction terminology is a nuanced landscape where precise definitions matter significantly. According to ALA Journals, certain subgenres like cozy mysteries are frequently undervalued or misclassified, creating challenges in literary scholarship and reader understanding.
Some of the most common terminology mistakes in mystery fiction include:
- Hardboiled vs. Detective Fiction: Often incorrectly used interchangeably
- Cozy Mystery vs. Traditional Mystery: Frequently confused despite distinct characteristics
- Thriller vs. Mystery: Misunderstood as synonymous genres
- Police Procedural vs. Detective Fiction: Subtle but important distinctions often overlooked
Bodhi Journals highlights the critical need for precise definitions, especially in academic and literary contexts. The conflation of hardboiled and detective fiction represents a prime example of how imprecise terminology can muddy our understanding of literary genres. Readers and scholars alike must pay careful attention to the nuanced differences between seemingly similar mystery subgenres.

For readers seeking to deepen their understanding of these complex distinctions, our guide on subtle literary classifications offers comprehensive insights into the intricate world of mystery fiction terminology.
Unlock the Mystery with Engaging Short Reads Tailored for You
Struggling to keep track of mystery fiction terminology like red herrings, cozy mysteries, and inverted detective stories can make enjoying the genre frustrating. If you love diving into complex puzzles or crave captivating stories featuring amateur sleuths and brilliant detectives but find traditional novels too time-consuming, our collection of mystery fiction short reads is designed just for you. Experience thrilling narratives that respect your busy schedule while immersing you in the exact subgenres and archetypes you enjoy.

Discover the perfect blend of intrigue and clarity with our Weekend Mystery Bundle. Featuring a carefully curated selection of cozy mystery short reads, murder mystery novellas, and detective short reads, you will embrace your passion for mystery fiction without getting lost in confusing terms or overwhelming plots. Don’t wait to transform your reading experience. Explore our collection now at theShortReads.com and decode mysteries effortlessly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is mystery fiction?
Mystery fiction is a literary genre that revolves around an enigmatic event, typically a crime, that remains unsolved until the story’s conclusion. It often features a detective who uses logical reasoning to unravel the mystery.
What are common terminology used in mystery fiction?
Key terms in mystery fiction include ‘detective’ (the investigator), ‘red herring’ (misleading clues), ‘MacGuffin’ (a plot-driving object), and ‘unreliable narrator’ (a storyteller with questionable credibility).
What are the major subgenres of mystery fiction?
Major subgenres of mystery fiction include detective fiction, cozy mystery, locked-room mystery, true crime, and police procedural, each offering unique storytelling styles and themes.
How do red herrings function in mystery storytelling?
Red herrings are deliberately misleading clues designed to distract readers from the actual solution. They create tension and engage readers by maintaining uncertainty about the outcome.
Recommended
- Understanding Mystery Fiction Terminology Explained – TheShortReads.com
- Mystery Fiction – TheShortReads.com
- Short Mystery Writing Tips for Captivating Tales – TheShortReads.com
- 7 Smart Ways to Discover Mystery Fiction for Men – TheShortReads.com
Psychological Thriller Explained: Key Elements and Types

Psychological thrillers grip us with more than nail-biting suspense. This genre pulls readers into the hidden corners of the mind, turning the ordinary into something far more unsettling. Studies show these stories are among the most popular in modern fiction, thanks to their focus on psychological tension and complex characters. If you want to understand what makes psychological thrillers so impactful, exploring their core elements and storytelling secrets opens a window into the thrill that keeps audiences hooked.
Table of Contents
- Defining Psychological Thrillers And Core Concepts
- Major Subtypes And Genre Variations
- Essential Storytelling Techniques Used
- Recurring Themes And Character Archetypes
- Common Pitfalls And What Readers Should Know
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Psychological Depth | Psychological thrillers focus on complex characters and their internal conflicts rather than external action. |
| Genre Variations | Subtypes like domestic noir and horror-of-personality offer unique insights into human psychology and narrative structure. |
| Narrative Techniques | Techniques such as unreliable narration and symbolic visual metaphors enhance the psychological experience for the audience. |
| Cautionary Elements | Readers should be aware of narrative clichés and representational challenges within the genre to fully appreciate its depth. |
Defining Psychological Thrillers and Core Concepts
Psychological thrillers represent a riveting genre that delves deep into the intricate labyrinths of human consciousness. According to en.wikipedia.org, these narratives combine elements of thriller and psychological fiction, focusing intensely on characters’ mental states, perceptions, and complex interpersonal dynamics.
At their core, psychological thrillers explore profound psychological landscapes that challenge traditional narrative boundaries. As research from ijnrd.org reveals, these stories immerse audiences in gripping narratives that expose characters’ deepest delusions, insecurities, and unresolved traumas. The genre masterfully blends elements of horror, mystery, and psychological investigation to create uniquely tension-filled experiences.
The key characteristics of psychological thrillers include:
- Intense psychological manipulation
- Exploration of unstable mental states
- Complex character motivations
- Blurred lines between reality and perception
- Deep investigations into human consciousness
Unlike traditional thriller genres, psychological thrillers prioritize internal conflict over external action. They transform the human mind into a battlefield, where characters wrestle with their own fears, secrets, and psychological demons. psychological motifs play a critical role in constructing these intricate narrative experiences, revealing how perception can become both a weapon and a vulnerability.
These narratives often challenge readers by presenting scenarios where nothing is as it initially appears. Mental instability, unreliable narrators, and psychological transformations become the primary storytelling mechanisms, creating an atmosphere of persistent uncertainty and psychological tension.
Major Subtypes and Genre Variations
Psychological thrillers encompass a rich and diverse landscape of narrative approaches, each subgenre offering unique insights into human psychology. According to en.wikipedia.org, the horror-of-personality subgenre represents a particularly intense exploration of psychological darkness, focusing on human villains with profoundly disturbing mental landscapes.
One compelling variation is domestic noir, which en.wikipedia.org describes as a subgenre centered on the dark undercurrents of intimate relationships. This approach transforms seemingly ordinary domestic settings into psychological minefields, revealing the complex emotional tensions lurking beneath surface normalcy.
The major subtypes of psychological thrillers include:
- Horror-of-Personality: Emphasizing psychological depth of human villains
- Domestic Noir: Exploring intimate relationship dynamics
- Paranoid Thrillers: Focusing on characters’ deepening sense of existential threat
- Cognitive Dissonance Narratives: Challenging characters’ perception of reality
- Trauma-Based Psychological Thrillers: Investigating unresolved psychological wounds
Each subtype approaches psychological tension through distinct narrative strategies. Paranoid thrillers, for instance, create suspense by gradually eroding characters’ sense of safety, while cognitive dissonance narratives deliberately destabilize audience expectations about narrative reality. psychological transformation becomes a critical lens through which these stories explore the fragility of human perception.
These genre variations share a fundamental commitment to excavating the complex interior worlds of characters. They transform psychological exploration into a high-stakes narrative adventure, where mental and emotional landscapes become more dangerous and unpredictable than any external threat.
![]()
Essential Storytelling Techniques Used
Psychological thrillers deploy a sophisticated arsenal of narrative techniques designed to penetrate the deepest recesses of human psychology. According to en.wikipedia.org, these narratives masterfully employ unreliable narrators and intricate plot twists to create a dissolving sense of reality that keeps audiences perpetually unsettled and emotionally invested.
Visual and atmospheric storytelling plays a crucial role in psychological thrillers. Research from ijnrd.org reveals how directors use symbolic elements like mirrors and strategic lighting techniques to externalize characters’ inner psychological landscapes. Low-key lighting and shadow play become powerful tools for portraying emotional turmoil, transforming visual aesthetics into a metaphorical representation of characters’ mental states.

The key storytelling techniques in psychological thrillers include:
- Unreliable Narration: Challenging audience perception
- Symbolic Visual Metaphors: Representing psychological states
- Non-Linear Narrative Structures: Disrupting chronological storytelling
- Psychological Fragmentation: Depicting mental breakdown
- Sensory Manipulation: Creating disorienting audience experiences
These narrative strategies work in concert to create a profoundly immersive psychological experience. By deliberately destabilizing traditional storytelling conventions, psychological thrillers transform narrative itself into a psychological exploration.
effective storytelling becomes a lens through which complex human experiences are examined and transformed.
Ultimately, the most powerful technique in psychological thrillers is their ability to blur boundaries between external reality and internal perception. They invite audiences to question not just what is happening, but how and why characters experience their reality in such uniquely fractured and compelling ways.
Recurring Themes and Character Archetypes
Psychological thrillers explore a complex tapestry of human experience through deeply nuanced themes and intricate character dynamics. According to en.wikipedia.org, these narratives frequently delve into profound psychological territories like death, identity, perception, and the malleable nature of reality, creating intense explorations of human consciousness.
The genre’s character archetypes are particularly fascinating. en.wikipedia.org highlights the emergence of characters like the femme fatale and the unreliable narrator, who challenge traditional storytelling by embodying psychological complexity. These characters often operate within intricate domestic landscapes, transforming seemingly ordinary relationships into psychological battlegrounds of manipulation and hidden motivations.
The most prevalent themes and character archetypes include:
- Themes:
- Psychological Disintegration
- Identity Crisis
- Manipulation and Betrayal
- Perception vs. Reality
- Moral Ambiguity
- Character Archetypes:
- The Obsessive Detective
- The Psychologically Fractured Protagonist
- The Manipulative Antagonist
- The Unreliable Witness
- The Psychological Predator
Unlike traditional narrative forms, psychological thrillers reject simplistic character representations. emotional storytelling becomes a critical lens through which these complex characters are examined, revealing the intricate psychological mechanisms that drive human behavior.
Ultimately, these themes and archetypes serve a profound purpose: they strip away social masks, exposing the raw, often uncomfortable truths about human nature. By presenting characters who exist in psychological gray areas, these narratives challenge audiences to confront the complexity of human motivation and the thin line between sanity and psychological breakdown.
Common Pitfalls and What Readers Should Know
Psychological thrillers, while compelling, are not immune to narrative traps that can undermine their psychological depth. According to en.wikipedia.org, the genre frequently struggles with predictable plot twists and overused narrative devices that can diminish the intellectual and emotional impact of the story.
Research from ijnrd.org highlights a critical concern about the genre’s representation, particularly the problematic perpetuation of stereotypes. The femme fatale archetype, for instance, often reinforces harmful narratives about women’s sexuality and psychological complexity, reducing nuanced characters to simplistic, potentially damaging tropes.
Key pitfalls readers should be aware of include:
- Narrative Weaknesses:
- Overly predictable plot structures
- Reliance on clichéd psychological tropes
- Shallow character development
- Unrealistic psychological representations
- Excessive reliance on shock value
- Representational Challenges:
- Stereotypical character archetypes
- Oversimplification of mental health experiences
- Sensationalization of psychological trauma
- Limited diversity in character perspectives
- Romanticization of dysfunctional behaviors
7 Essential Psychological Thriller Tips for Every Reader can help readers develop a more critical and nuanced approach to navigating these potential narrative pitfalls.
Ultimately, discerning readers should approach psychological thrillers with both intellectual curiosity and critical awareness. By recognizing these potential limitations, audiences can engage more deeply with the genre’s true potential: exploring the complex, often uncomfortable terrain of human psychological experience.
Dive Deeper Into Psychological Thrillers With Short Reads Designed to Engage Your Mind
If you find yourself captivated by the complex mental games and blurred realities described in psychological thrillers this is your chance to experience these elements firsthand. This genre’s challenges such as navigating unreliable narrators and exploring fractured perceptions can sometimes feel overwhelming but also intensely rewarding. Our collection of psychological thriller short reads offers sharp insights and engrossing stories that perfectly capture the essence of manipulation betrayal and identity crisis found in these narratives.

Explore our selection today by visiting The Weekend Mystery Bundle. With titles carefully crafted to highlight intricate character psychology and thrilling plot twists you’ll find the perfect balance between emotional storytelling and gripping suspense. Don’t wait to immerse yourself in stories that challenge your perception and keep you guessing. Your next engaging psychological thriller awaits now at The Weekend Mystery Bundle. Discover how short reads can transform your understanding of this captivating genre.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main characteristics of psychological thrillers?
Psychological thrillers are characterized by intense psychological manipulation, exploration of unstable mental states, complex character motivations, and blurred lines between reality and perception. They prioritize internal conflict, focusing on characters’ fears, secrets, and psychological demons.
What are the common subtypes of psychological thrillers?
The major subtypes include Horror-of-Personality, Domestic Noir, Paranoid Thrillers, Cognitive Dissonance Narratives, and Trauma-Based Psychological Thrillers. Each subtype explores psychological tension through unique narrative strategies.
What storytelling techniques are commonly used in psychological thrillers?
Key storytelling techniques in psychological thrillers include unreliable narration, symbolic visual metaphors, non-linear narrative structures, psychological fragmentation, and sensory manipulation. These techniques create an immersive and unsettling experience for the audience.
What are some recurring themes and character archetypes in psychological thrillers?
Recurring themes include psychological disintegration, identity crisis, manipulation and betrayal, perception vs. reality, and moral ambiguity. Common character archetypes feature the obsessive detective, psychologically fractured protagonist, manipulative antagonist, unreliable witness, and psychological predator.
ShareWhy Novellas Are Popular: Complete Reader Guide

Nearly every avid reader has discovered the sweet spot between short stories and lengthy novels, where novellas shine. These compact works pack the emotional punch and depth of full novels into a format that rarely exceeds 50,000 words. For time-pressed readers, novellas offer an immersive escape without the marathon commitment, making them more appealing than ever. This guide reveals what sets novellas apart, clears up common misconceptions, and spotlights why their unique structure captures global audiences.
Table of Contents
- Novellas Defined: Core Features And Myths
- Types Of Novellas In Mystery And Thriller
- How Novellas Fit Busy Modern Lifestyles
- Appeal To Diverse And Global Audiences
- Novellas Versus Novels And Short Stories
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Defining Characteristics | Novellas, distinct from novels and short stories, typically focus on a single conflict, feature condensed character development, and can be read in one sitting. |
| Popularity Growth | The increasing demand for immersive yet quick narratives makes novellas appealing to busy readers seeking convenience without compromising storytelling quality. |
| Genre Versatility | Mystery and thriller novellas encompass various subgenres, each providing unique storytelling experiences while maintaining fast-paced narratives. |
| Cultural Accessibility | Novellas allow for diverse themes and global perspectives, making them accessible to a broad audience through their concise format and universal appeal. |
Novellas Defined: Core Features And Myths
A novella occupies a unique literary space between short stories and full-length novels, offering readers a compact yet immersive narrative experience. According to Wikipedia, the term originates from the Italian word ‘novella’, meaning ‘new’, and represents a prose fiction form with distinct structural characteristics that set it apart from longer and shorter written works.
Novellas are characterized by several core features that distinguish them from traditional novels and short stories. As research from University of Babylon indicates, these narratives typically possess the following attributes:
- Focused Narrative: Concentrates on a single primary conflict or theme
- Condensed Character Development: Fewer characters compared to novels
- Compact Length: Designed to be read in one sitting
- Realistic Tone: Often satirical or grounded in realistic storytelling
- Minimal Chapter Structure: Generally lacks traditional chapter divisions
Contrary to common myths, novellas are not simply ‘shorter novels’ but sophisticated literary forms with their own narrative integrity. They require precise storytelling skills, demanding authors craft complex narratives within limited word counts.
 Writers must strategically develop characters, advance plot, and create meaningful narrative arcs without the expansive canvas of a full novel.
Writers must strategically develop characters, advance plot, and create meaningful narrative arcs without the expansive canvas of a full novel.
The popularity of novellas continues to grow, particularly among busy readers and those seeking immersive storytelling experiences that can be consumed quickly. Short Reads vs Novellas: Everything You Need to Know provides deeper insights into why these compact narratives have captured readers’ imaginations across various genres and reading preferences.
Types Of Novellas In Mystery And Thriller
Mystery and thriller novellas represent a dynamic and captivating literary genre that delivers intense storytelling within a compact narrative framework. According to MWEditing, these narratives are characterized by fast-paced plots, intriguing mysteries, and suspenseful twists that keep readers engaged through unexpected revelations and gripping storylines.
The mystery and thriller novella landscape encompasses several distinctive subgenres, each offering unique storytelling approaches:
- Hard-Boiled Mysteries: Urban settings with complex moral landscapes
- Cozy Mysteries: Lighthearted narratives with less graphic violence
- Psychological Thrillers: Deep explorations of character mental states
- Political Thriller Novellas: Intrigue centered around governmental or institutional conflicts
- Detective Short Reads: Compact investigations with focused narrative arcs
As MasterClass explains, each subgenre brings its own distinctive elements to the novella format. Hard-boiled mysteries often feature morally ambiguous urban landscapes, while cozy mysteries provide gentler, more lighthearted narrative experiences that appeal to readers seeking less intense storytelling.
For readers seeking immersive yet quick reading experiences, thriller novellas offer the perfect balance of suspense and concise storytelling. These compact narratives allow readers to experience complete, intricate stories without the time commitment of full-length novels, making them ideal for busy mystery enthusiasts who crave compelling narratives in bite-sized formats.
How Novellas Fit Busy Modern Lifestyles
In today’s fast-paced world, reading time is a precious commodity, and novellas have emerged as the perfect literary solution for time-strapped book lovers. According to MWEditing, these compact narratives cater specifically to readers with limited time by offering concise yet complete stories that can be consumed in a single sitting.
The unique advantages of novellas for busy individuals include:
- Quick Consumption: Complete stories readable in one sitting
- Minimal Time Investment: Shorter than traditional novels
- High-Intensity Narratives: Concentrated plot and character development
- Flexible Reading: Perfect for commutes, lunch breaks, or short leisure moments
- Storytelling Efficiency: Maximum narrative impact with minimum time commitment
Research from University of Babylon confirms that novellas are strategically designed to provide full narrative experiences without demanding extensive time investments. This makes them particularly attractive to professionals, students, and anyone struggling to balance reading with demanding schedules.
For those seeking practical reading strategies that align with modern lifestyle constraints, short reads benefits guide offers additional insights into maximizing literary enjoyment within limited timeframes. Novellas represent more than just shorter books – they’re a sophisticated reading approach tailored for contemporary readers who refuse to compromise on storytelling quality despite time limitations.
Appeal To Diverse And Global Audiences
Novellas represent a powerful literary form that transcends cultural boundaries, offering a unique storytelling experience that resonates with readers across different backgrounds and languages. According to MWEditing, the concise format allows authors to explore diverse themes and settings, making these compact narratives remarkably accessible to a global readership.
The universal appeal of novellas is rooted in several key characteristics that make them attractive to diverse audiences:
- Linguistic Accessibility: Easier translation due to shorter length
- Cultural Flexibility: Adaptable narratives that cross geographical boundaries
- Thematic Universality: Exploration of fundamental human experiences
- Economic Reading: Affordable and less time-consuming for international readers
- Genre Diversity: Wide range of storytelling styles and perspectives
Research from University of Babylon highlights the novella’s historical influence across European literary traditions, demonstrating its remarkable ability to create realistic narratives that resonate with diverse audiences. The compact format allows for nuanced storytelling that can bridge cultural differences while maintaining narrative intensity.
For readers seeking global perspectives, mystery novellas offer an exceptional window into different cultural experiences, providing rich storytelling without the significant time investment of full-length novels. This unique literary form continues to break down cultural barriers, offering readers a sophisticated yet accessible approach to understanding diverse human experiences.
Novellas Versus Novels And Short Stories
The literary landscape is rich with diverse narrative forms, each offering unique storytelling experiences. According to Wikipedia, novellas occupy a distinctive middle ground, characterized by a length that falls between short stories and full-length novels, creating a compelling format that captures readers’ imagination with remarkable precision.
Key differences between novellas, novels, and short stories include:
- Length: Novellas range from 30,000 to 50,000 words, compared to novels (over 50,000 words) and short stories (under 7,500 words)
- Narrative Complexity: More developed than short stories, less intricate than novels
- Character Development: Focused character arcs with limited but deep exploration
- Plot Structure: Single primary conflict versus multiple subplots in novels
- Reading Time: Typically completed in one sitting
Research from University of Babylon emphasizes that while novels generally extend beyond 200 pages with complex narrative structures, novellas offer a more concentrated storytelling experience. They provide readers with a complete narrative journey without the extensive time commitment required by full-length novels.

For readers seeking a deeper understanding of these literary distinctions, Novellas vs. Novels: Complete Guide to Key Differences offers comprehensive insights into the nuanced world of narrative formats. Novellas ultimately represent a sophisticated middle ground, delivering rich storytelling with exceptional narrative efficiency.
Discover Perfect Novellas That Fit Your Busy Life and Mystery Cravings
Finding time to enjoy a captivating story can be tough when life moves fast. This article highlights how novellas meet the challenge by offering quick yet immersive storytelling with focused narratives and intense plots. Whether you are drawn to cozy mysteries, psychological thrillers, or political intrigue, the compact format of novellas lets you experience rich characters and suspenseful twists without a huge time commitment.
Enjoy the emotional excitement of a complete story in one sitting by exploring our Weekend Mystery Bundle.

Dive into a collection curated for readers who value both quality and convenience. From cozy mystery short reads to murder mystery novellas, our selections bring you intense plotlines and carefully crafted characters ready to thrill and entertain. Start your novella journey now at The Short Reads and experience the perfect balance of suspense and brevity tailored for your lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines a novella compared to a novel and a short story?
A novella typically ranges from 30,000 to 50,000 words, offering a more developed narrative than a short story (under 7,500 words) but less complexity than a full-length novel (over 50,000 words). It focuses on a single conflict and allows for concentrated character development within a compact format.
Why are novellas appealing to busy readers?
Novellas are designed for quick reading, allowing busy individuals to complete a story in one sitting. Their concise narratives provide high-intensity storytelling with minimal time investment, making them ideal for readers looking to fit literature into hectic schedules.
What are the main themes explored in mystery and thriller novellas?
Mystery and thriller novellas often explore themes such as crime, morality, psychological tension, and political intrigue. They captivate readers with fast-paced plots, unexpected twists, and a focus on single primary conflicts that draw readers into the narrative.
How do novellas resonate with a global audience?
Novellas are linguistically and culturally accessible due to their shorter length, making them easier to translate and adapt across different cultural contexts. Their universal themes, such as fundamental human experiences, appeal to diverse audiences, allowing readers worldwide to engage with a variety of storytelling perspectives.
Recommended
- The Essential Guide to the Role of Novellas in Fiction – TheShortReads.com
- Novellas vs. Novels: Complete Guide to Key Differences – TheShortReads.com
- Short Reads vs Novellas: Everything You Need to Know – TheShortReads.com
Novellas vs. Novels: Complete Guide to Key Differences

A novella offers a unique middle ground in fiction, packing a punch with its concise storytelling. For many readers and writers, knowing whether a story is best told as a novella or a novel can shape the entire reading experience. With novels typically exceeding 50,000 words and novellas ranging from 20,000 to 40,000 words, these two forms provide distinct ways to explore characters and worlds. Understanding their differences helps you choose the right path for your next literary adventure.
Table of Contents
- Defining Novellas And Novels: Core Differences
- Length, Structure, And Narrative Scope
- Genre Trends In Novellas And Novels
- Audience Appeal And Reader Experiences
- Choosing Between Novellas And Novels
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Length and Complexity | Novellas range from 20,000 to 40,000 words, while novels start at 50,000 words, with the former focusing on a single theme and the latter allowing for intricate plots. |
| Genre Suitability | Novellas excel in concise genres like romance and mystery, whereas novels are suited for expansive explorations like epic fantasy and historical fiction. |
| Reading Experience | Novels deliver immersive storytelling appealing to deep character exploration, while novellas provide quick, impactful narratives ideal for busy readers. |
| Choosing Format | Select a novella for focused narratives and limited complexity, and a novel for multi-dimensional storytelling and extensive world-building. |
Defining Novellas and Novels: Core Differences
Understanding the fundamental differences between novellas and novels is crucial for readers and writers alike. According to research from naac.psou.ac.in, a novella is a prose fiction that sits uniquely between a short story and a novel, characterized by its focused narrative approach and limited scope.
Novella Characteristics
- Typically shorter than a traditional novel
- Concentrates on a single incident or core theme
- Features one or two primary characters
- Often set in a single location
- Can usually be read in one sitting
Novels, in contrast, provide a more expansive storytelling landscape. As detailed by uobabylon.edu.iq, novels are extensive narratives exceeding 40,000 words, enabling authors to craft intricate plots and develop complex character arcs. While novellas maintain a tightly focused narrative, novels allow writers to explore multiple storylines, introduce numerous characters, and delve deeper into thematic explorations.
Novel Characteristics
- Longer narrative format
- Supports complex, multi-layered plots
- Allows extensive character development
- Can include multiple subplots and perspectives
- Generally structured with distinct chapters
The primary distinguishing factor between novellas and novels lies in their narrative complexity and length. Short Reads vs Full Novels: Complete Guide offers additional insights into how these different formats serve unique storytelling purposes. Novellas provide a concentrated, intense reading experience, while novels offer a more immersive and expansive journey through fictional worlds.
Length, Structure, and Narrative Scope
The distinction between novellas and novels becomes most apparent when examining their length, structural complexity, and narrative scope. According to ballard-tighe.com, novels typically start at 50,000 words, offering substantial space for comprehensive storytelling, while novellas range from 20,000 to 40,000 words, providing a more concentrated narrative experience.
Word Count Breakdown
- Novels: 50,000+ words
- Novellas: 20,000 to 40,000 words
- Short Stories: Under 7,500 words
Research from spines.com highlights the fundamental difference in narrative approach. Novellas maintain a narrow focus, concentrating on a single central theme, character, or event, often avoiding the complexity of multiple subplots. Novels, conversely, offer expansive storytelling real estate, enabling writers to weave intricate narratives with multiple characters, rich settings, and interconnected storylines.
Structural Characteristics
- Novels support complex, multi-layered plots
- Novellas maintain a streamlined, focused narrative
- Novels can include extensive character backstories
- Novellas typically explore one primary character arc
For writers and readers seeking more insights into compact storytelling formats, Understanding Short Story Structure: A Deep Dive provides additional context about narrative design across different literary forms. The key takeaway is that while novels offer a panoramic view of a fictional world, novellas provide an intimate, concentrated exploration of a specific narrative moment or character experience.

Genre Trends in Novellas and Novels
Genre selection plays a critical role in determining whether a story is best suited as a novella or a full-length novel. According to aspiringwriteracademy.com, novellas excel in genres that benefit from concise, focused storytelling, such as romance, mystery, and suspense.
Ideal Genres for Novellas
- Romance
- Mystery
- Suspense
- Psychological thrillers
- Tight character studies
Research from inca.ac.id reveals that novellas are particularly effective when concentrating on a singular, central theme or conflict. In contrast, novels provide expansive narrative landscapes that accommodate complex world-building and multiple interconnected storylines, making them perfect for genres requiring deeper exploration.
Ideal Genres for Novels
- Epic fantasy
- Historical fiction
- Science fiction
- Complex family sagas
- Multi-generational narratives
For readers interested in exploring compact storytelling formats, Short Reads vs Novels: Complete Guide for Readers offers additional insights into how different genres leverage various narrative lengths. The key distinction remains that novellas offer intense, concentrated storytelling, while novels provide room for intricate narrative development across multiple plot dimensions.
Audience Appeal and Reader Experiences
The reading experience fundamentally differs between novellas and novels, with each format offering unique engagement for different types of readers. According to differencess.com, novels provide immersive, multi-dimensional storytelling that appeals to readers who enjoy deep character exploration and complex narrative landscapes.
Reader Preferences
- Novels: Readers seeking comprehensive stories
- Novellas: Readers wanting quick, impactful narratives
- Short Stories: Readers desiring ultra-condensed experiences
Research from askbib.com highlights that novellas deliver concise narratives focusing on a single theme or character arc, offering quick yet powerful reading experiences. These compact stories are perfect for busy readers or those seeking concentrated emotional and intellectual engagement without the time commitment of a full novel.

Reading Time Considerations
- Novellas: 1-3 hours reading time
- Novels: 6-12 hours reading time
- Short Stories: Under 1 hour
For readers interested in exploring different storytelling formats, Understanding the Benefits of Short Reads provides additional insights into why compact narratives can be just as compelling as their longer counterparts. The beauty of both formats lies in their ability to transport readers into distinct worlds, whether through a concentrated burst of storytelling or an expansive, immersive journey.
Choosing Between Novellas and Novels
Deciding between writing a novella or a novel requires careful consideration of your story’s core elements and narrative ambitions. According to aspiringwriteracademy.com, critical factors include the complexity of plot, number of characters, and depth of character development.
Key Decision Factors
- Plot complexity
- Character count
- Narrative depth
- Time investment
- Thematic exploration
Research from spines.com suggests that novellas are ideal for focused narratives centered on a single theme or event, while novels provide expansive terrain for exploring multiple storylines and intricate character arcs. Think of a novella as a precise, targeted storytelling approach versus a novel’s panoramic narrative landscape.
Selection Criteria
- Choose novella if:
- Story centers on single character/event
- Limited plot complexity
- Tight narrative focus desired
- Choose novel if:
- Multiple character perspectives
- Complex, interconnected plot
- Extensive world-building needed
For writers seeking additional guidance in selecting the right format, Best Short Books offers insights into crafting compelling narratives across different story lengths. The ultimate decision hinges on your story’s unique requirements and the emotional journey you want to create for your readers.
Discover the Perfect Fit for Your Reading Taste Between Novellas and Novels
If you have ever felt torn between quick, immersive stories and expansive narratives then this guide on “Novellas vs. Novels” clearly highlights the challenge many readers face. The key hurdle is finding a story with the right balance of length and complexity to match your time and mood without sacrificing depth or engagement. Whether you want a focused thriller or a layered plot with multiple characters the right format makes all the difference.
Explore our curated collection of psychological thriller short reads, murder mystery novellas, and detective short reads crafted to deliver precisely that sharp narrative punch or the immersive experience you crave.

Dive into gripping stories that fit your lifestyle right now at The Short Reads. Take control of your reading journey with our handpicked selection and see why countless readers choose quality over quantity today! Don’t wait to experience storytelling that fits your pace and sparks your imagination. Start browsing now and find your next captivating read at online short reads.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between a novella and a novel?
The primary difference lies in length and narrative complexity: novellas are typically 20,000 to 40,000 words and focus on a single incident or theme, while novels exceed 50,000 words and support complex, multi-layered plots with multiple characters and subplots.
How long does it typically take to read a novella compared to a novel?
Novellas usually take 1-3 hours to read, whereas novels can require 6-12 hours, depending on their length and complexity.
What genres are best suited for novellas?
Novellas excel in genres that benefit from concise storytelling, such as romance, mystery, suspense, and psychological thrillers, focusing on a singular theme or character arc.
How do I decide whether to write a novella or a novel?
Consider factors such as plot complexity, character count, narrative depth, and the emotional journey you want to create. If your story centers on a single event or has limited complexity, a novella may be ideal. For more intricate narratives with multiple perspectives, a novel is the better choice.
Recommended
- Short Reads vs Full Novels: Complete Guide – TheShortReads.com
- Short Reads vs Novels: Complete Guide for Readers – TheShortReads.com
- What is Flash Fiction? Understanding This Unique Story Form – TheShortReads.com
- 7 Mystery Fiction Types for Learners and Busy Readers – TheShortReads.com
